


研究方向
IDS(艾杜糖醛酸2-硫酸酯酶)是一种溶酶体酶,在硫酸皮肤素和硫酸乙酰肝素的降解途径中发挥着至关重要的作用。作为细胞代谢的重要组成部分,IDS 促进溶酶体内这些糖胺聚糖的分解,有助于维持正常的细胞功能和组织稳态。IDS 的酶活性对于硫酸皮肤素和硫酸乙酰肝素的分解代谢至关重要,可防止它们在溶酶体内积聚并确保正常的细胞过程。这强调了 IDS 在参与糖胺聚糖降解的复杂代谢途径网络中的关键作用。
Measured by its ability to hydrolyze the substrate 4- Nitrocatechol Sulfate (PNCS). The specific activity is > 1.0 pmol/min/µg, as measured under the described conditions.
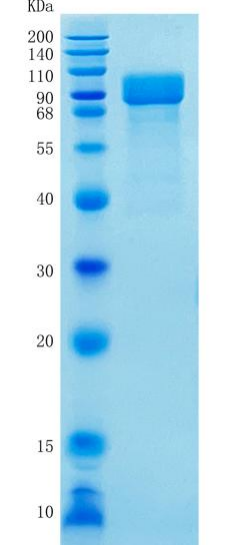
As a member of the sulfatase family, IDS is required for the lysosomal degradation of the glycosaminoglycans (GAG) heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate (2, 3). It hydrolyzes the 2-sulfate group of the L-iduronate 2-sulfate units of the GAG. The IDS deficiency results in mucopolysaccharidosis II (MPS II or Hunter syndrome), an X-linked inborn error leading to lysosomal accumulation of the GAG and its excretion in urine. MPS II has a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations ranging from mild to severe. The deduced amino acid sequence of human IDS consists of a signal peptide (residues 1‑25), a pro peptide (residues 26‑33) and a mature chain (residues 34‑550) that may be further processed into the 42 kDa chain (residues 34‑455) and the 14 kDa chain (residues 456‑550) . rhIDS corresponds to the single chain and has sulfatase activity described above.